Making batteries safer by understanding the important thing thermodynamic variations between the most well-liked cell chemistries
Whereas NMC cells dominate the present technology of US and European BEVs, rising price pressures are forcing OEMs to take a tougher take a look at LFPs. Regardless of their decrease power density, LFP cells are nonetheless vulnerable to single-cell thermal runaway, and controlling its propagation to adjoining cells stays a prime precedence. To correctly handle thermal runaway propagation (TRP), pack designers should first perceive the three key thermodynamic variations between the 2 cell sorts.
First, NMC cells set off extra simply. The chart under exhibits two equally sized prismatic cells triggered into thermal runaway with an exterior heating pad. The NMC cell goes unstable at a temperature of 160°C, whereas the LFP holds regular as much as 230°C. This deeper thermal effectively, mixed with LFPs’ larger measurement and weight for a similar vary, gives an LFP pack with extra thermal mass than its NMC counterpart. The thermal mass of adjoining cells is likely one of the few benign pathways that stray power can take throughout a runaway occasion (the opposite being rejection by the pack’s cooling system). Whereas cell-to-cell conduction by itself can not soak up the complete brunt of a runaway occasion, thermal mass can present extra time for occupants to tug over and get away from the automobile.
Second, NMC cells burn hotter than LFPs. As soon as pushed into thermal runaway, the NMC cell-face temperature peaks at 800°C, whereas the LFP solely spikes to 620°C. That is considerably paradoxical since, regardless of their decrease power density, calorimetry exhibits that LFP cells typically have the next gasoline content material per amp-hour of storage capability. Nevertheless, as a result of NMCs smuggle extra elemental oxygen into the cell, their combustion effectivity and, due to this fact, warmth launch is greater.
Lastly, the ejection phenomena related to every cell chemistry are very totally different. When an NMC cell goes into thermal runaway, there tends to be a 10- to 30-second interval by which liquid, fuel, and stable supplies are violently ejected by the cell vent. These stable supplies are sometimes bits of aluminum, carbon, and burning plastic. So NMC cells convey all three parts of the hearth triangle – gasoline, oxygen, and an ignition supply – to a thermal runaway occasion. The ensuing torch-and-grit blast can burn by all however the sturdiest enclosure supplies and blankets the encompassing cells in flaming gases and particles. Managing these flows is likely one of the most troublesome points of designing a TRP-resistant NMC pack.
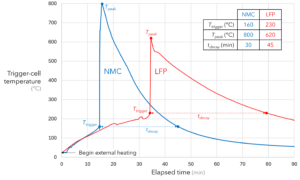
In distinction, LFP cells are likely to emit largely smoke and fuel which, though scorching, is usually not actively combusting. Whereas subsequent combustion and even explosions are doable, the inside of an LFP pack is usually oxygen-starved throughout a thermal runaway occasion, so these dangers exist primarily exterior the automobile. Additional, the overall mass ejected from an LFP thermal runaway is just 20-25% of the unique cell mass, versus 40-50% for an NMC. So, each the hazard degree and amount of LFP ejecta are decrease than that of NMC designs.
In brief, controlling thermal propagation in an NMC pack is primarily about fuel administration and secondarily about direct cell-to-cell warmth switch. In an LFP pack, that dynamic is reversed. That is lucky: with the arrival of aerogel thermal obstacles reminiscent of PyroThin cell obstacles, cell-to-cell warmth switch is now a solved downside. Managing combustion gases and flaming ejecta stays stubbornly onerous to deal with.
aerogel.com


